High Blood Pressure Medications
Choosing Blood Pressure Medication
Many drugs are available to treat high blood pressure. Choosing the right one can be tricky. Learn how to find the best one for you. There are a variety of antihypertensive medications that each come with their own advantages and disadvantages. Your healthcare provider may prescribe more than one type of medication to treat your condition. If you want to maintain a healthy blood pressure, it is important to take your medications as prescribed, monitor your blood pressure regularly, and make lifestyle changes as needed.
Lifestyle changes
If you're beginning to develop high blood pressure (prehypertension), lifestyle changes may help you reduce or eliminate your need for medication. If you already have high blood pressure, lifestyle changes may also help you lower your blood pressure.
Try these steps to help lower and control blood pressure.
- Eat a healthy diet with plenty of fruits and vegetables.
- Reduce the amount of salt (sodium) in your diet.
- Don't smoke.
- Manage stress.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Get regular exercise. Aim for 30 minutes of moderate activity on most days of the week. It's OK to break up your activity into three 10-minute sessions a day.
- Avoid or limit alcohol. If you choose to drink alcohol, do so in moderation. For healthy adults, that means up to one drink a day for women and up to two drinks a day for men.
Medication options
If your lifestyle changes are not enough to control your blood pressure, you will likely need to take blood pressure medication. Your doctor may prescribe one or more of these medications:
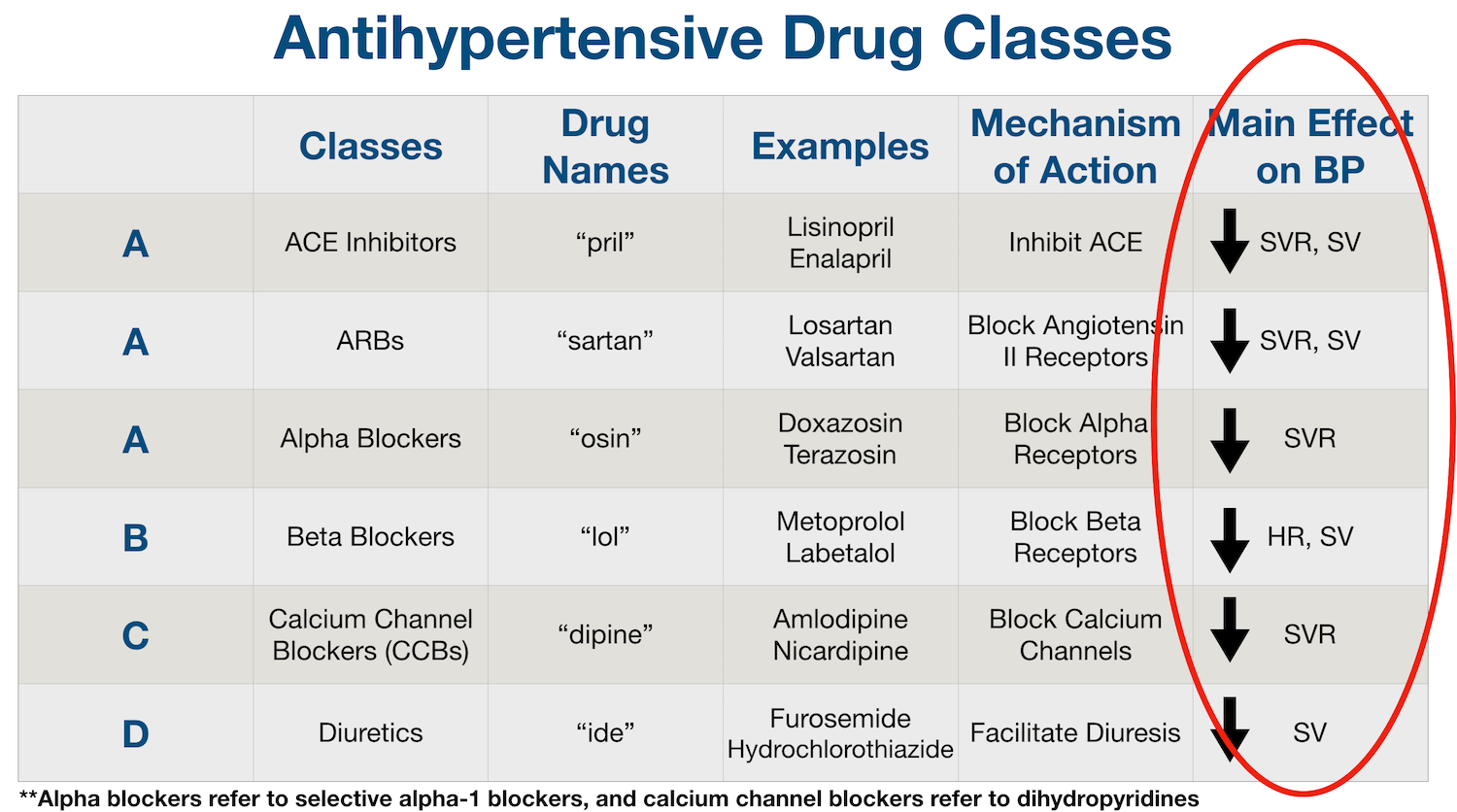
- Water pills (diuretics).
A diuretic is a medication that helps to remove excess water and sodium from the body. This can help to reduce the amount of fluid flowing through the veins and arteries, which can help to reduce pressure on the walls of the blood vessels.
There are three types of diuretics: thiazide, loop and potassium-sparing. If diuretics aren't enough to lower blood pressure, a health care provider might recommend adding other blood pressure medications to your treatment.
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors. ACE inhibitors work by preventing the formation of angiotensin, a body chemical that narrows blood vessels. This helps to relax blood vessels and improve blood flow.
- Angiotensin 2 receptor blockers (ARBs). These drugs block the action of angiotensin.
- Calcium channel blockers. There are a number of medications that can prevent calcium from entering cells, known as calcium channel blockers. These drugs can be useful in relaxing arteries and keeping them open.
- Beta blockers. Beta blockers can help to regulate the hormone epinephrine, also known as adrenaline. By blocking the effects of adrenaline, beta blockers can help to slow down the heart rate and reduce the force of heartbeats. This can be beneficial for people who suffer from conditions such as anxiety or high blood pressure.
- Renin inhibitors. Renin is a substance produced by the kidneys that triggers a series of steps that increases blood pressure. Inhibitors of renin slow the production of this substance.
Other medications sometimes used to treat high blood pressure
If you are not able to reach your blood pressure goal with one or more of the above medications, other drugs that lower blood pressure include:
- Alpha blockers.
The use of alpha blockers can help to prevent the hormone norepinephrine from causing the muscles in the walls of smaller arteries and veins to tighten, which in turn can help to keep the vessels open and relaxed.
- Alpha-beta blockers. Alpha-beta blockers work in a similar way to beta blockers. They may be prescribed if you have high blood pressure and are at risk of heart failure.
- Central-acting agents. Central-acting agents work by preventing the brain from sending signals to the nervous system that would normally speed up the heart rate and narrow the blood vessels. This action allows the heart to pump more efficiently and blood to flow more easily through the veins and arteries.
- Vasodilators. These medications help to prevent the muscles in the veins and arteries from tightening and narrowing. This, in turn, allows for blood to flow more easily and the heart doesn't have to work as hard.
- Aldosterone antagonists. Many medications used to treat high blood pressure work by blocking the hormone aldosterone. Aldosterone antagonists are a type of medication that can be used to prevent salt and fluid retention, which can contribute to high blood pressure. These medications are usually prescribed for people whose high blood pressure is difficult to control.
The effectiveness of a drug may vary depending on the person's age, sex, race, blood pressure level, and overall health. In general, combining two drugs works better than using a single drug to get blood pressure under control. Sometimes, additional medication may be needed to achieve a blood pressure goal.
High blood pressure drugs and other health conditions
High blood pressure is often associated with other health problems. Having high blood pressure increases the risk of developing one of the following conditions:
- Chronic kidney disease
- Coronary artery disease
- Diabetes
- Heart attack or stroke
- Heart failure
- Swelling or thickening of the left chamber of the heart (left ventricular hypertrophy)
A targeted treatment approach may help to reduce the risk of conditions such as chest pain and coronary artery disease. For example, a beta blocker may be recommended to lower blood pressure, prevent chest pain, and reduce heart rate.
If you have diabetes and high blood pressure, adding a diuretic to your existing ACE inhibitor medication may decrease your risk of a heart attack and stroke. If you have diabetes, high blood pressure and kidney disease, you may need an ACE inhibitor or an angiotensin 2 receptor blocker.
Reaching your blood pressure goal
A combination of lifestyle changes and medication is often needed to help control blood pressure. However, it may take some trial and error to find the medications or doses that work best for you. Monitoring your blood pressure at home can help you and your health care provider track your progress and see if your treatment plan is working. Home blood pressure monitors are widely available and relatively inexpensive, and you don't need a prescription to buy one.
This is a prescription discount plan. This is NOT insurance nor a Medicare prescription drug plan. The range of prescription discounts provided under this discount plan will vary depending on the prescription and pharmacy where the prescription is purchased and can be up to 85% off the cash price. You are fully responsible for paying your prescriptions at the pharmacy at the time of service, but you will be entitled to receive a discount from the pharmacy in accordance with the specific pre-negotiated discounted rate schedule.
All Rights Reserved | ScriptKingRX


